Understanding what electrostatic discharge (ESD) is, why it occurs, and how it affects electrical components is key to preventing unwanted damage in an electronics inspection or assembly environment. Let’s explore some common questions.
What is ESD?
ESD is caused when two objects with different voltage potentials – one negative, one positive – come into contact. For example, if you were to walk across a carpeted floor and touch a metal doorknob, the triboelectric charge that built up during your walk across the floor would cause a discharge, or shock, when you touched a metal doorknob with a different electrical potential.
Similarly, lighting is caused by clouds generating different electronic particles through friction between other clouds. Likewise, the earth has yet a different electrical potential due to it naturally being ground.
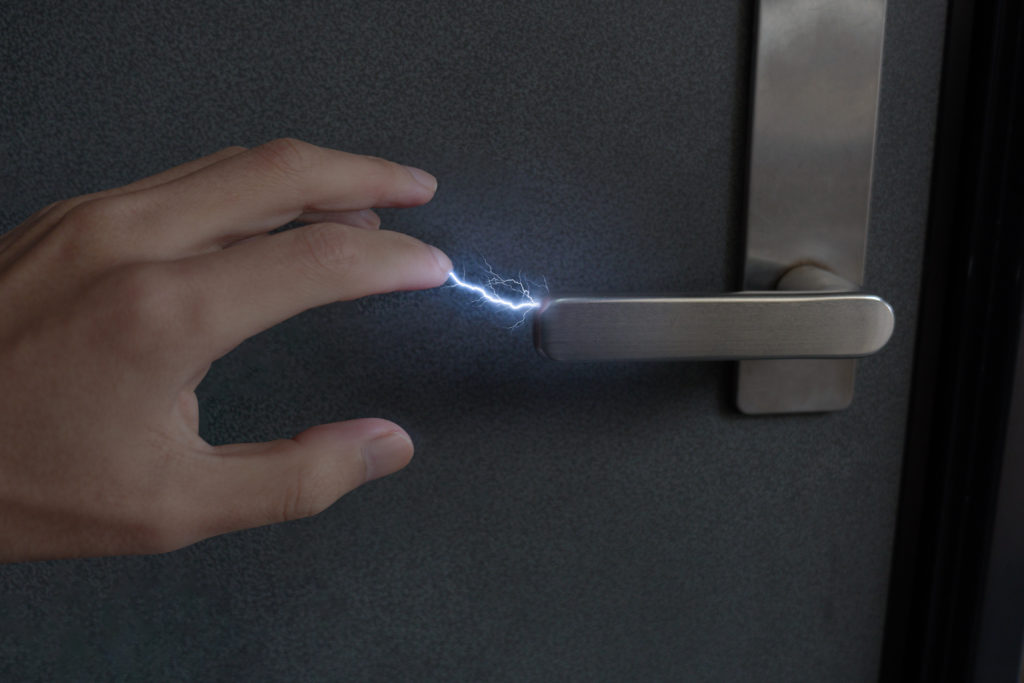


How does ESD affect the electronics manufacturing environment?
ESD to an electronic component can result in internal damage. While not always visible, this damage can lead to shortened component lifespan and premature failure of the component and the instrument in which the component is used.
Circuit boards are particularly susceptible to damage from ESD since the components when soldered, or being soldered, allow for numerous contact points and, therefore, numerous opportunities for ESD.
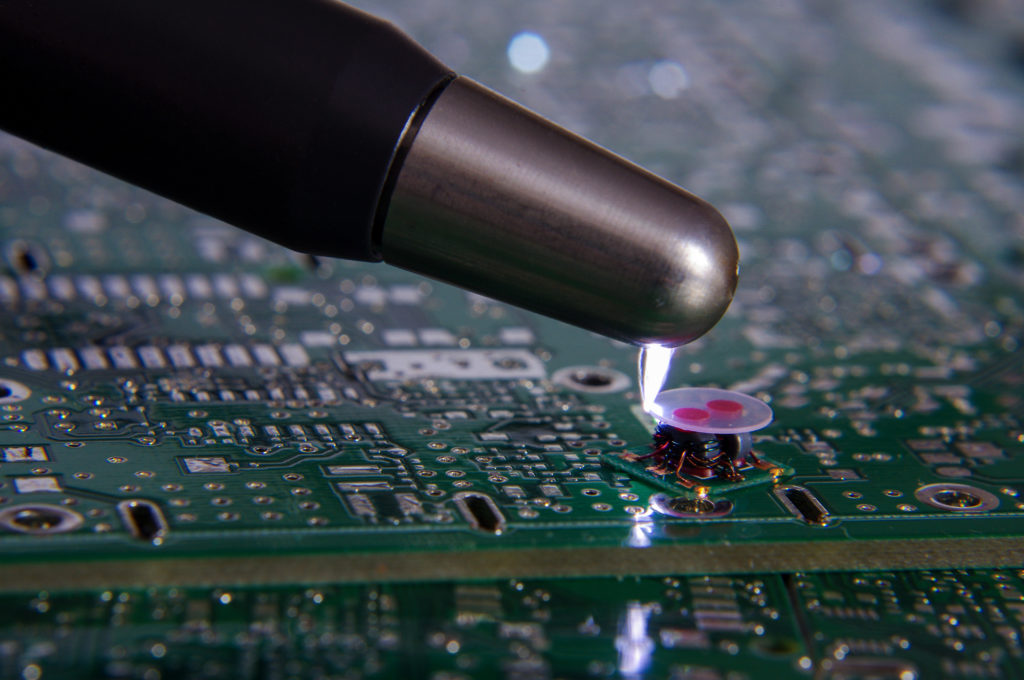
How do you prevent ESD in an electronics manufacturing environment?
- Create an environment where everything has the same electrical potential. To do so requires technicians be grounded by wearing wrist or heel straps that touch or are connected to an earth ground on the same worktable or an ESD work mat when handing circuit boards.
- Using all ESD-Safe equipment on a workbench will keep components and tools at a similar potential, thereby eliminating the threat of ESD discharge to a circuit board.
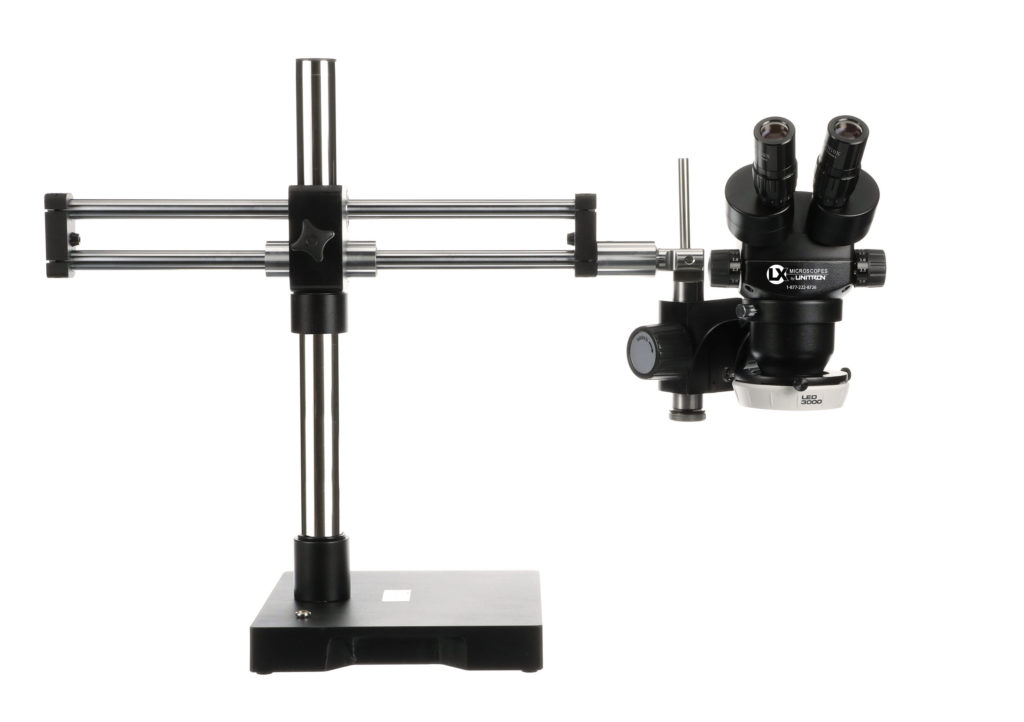
How are ESD-Safe LX Microscopes by UNITRON designed for use in static-sensitive environments?
To ensure continuity of the microscope system with the inspection environment, ESD-Safe LX Microscopes by UNITRON are coated with a metal-laced paint that measures 105Ω/sq. (static dissipative). ESD-Safe models include 10mm static grounding cables, metal boom stand bushings, and metal pads on the microscope base. Since the surfaces are no longer insulative, triboelectric charging results in drastically lower voltages by uniformly distributing any charge (under 50 volts) throughout the entire surface of the microscope.
LX Microscopes by UNITRON also offers an accessory ESD-Safe LED ring light featuring ESD-Safe construction with grounding cable, and delivering bright white illumination to the sample.

For more information about ESD-Safe LX Microscopes by UNITRON, including technical questions and distributor information, contact Customer Support at 631-543-2000 or info@unitronusa.com.